This blog is a blog that will going to be posting a physics related articles every week. The posts will explain about many things coming out from a Grade 8 2B science text book of Penerbit Erlangga™.
Sunday, 28 April 2013
Sunday, 21 April 2013
Vibration and Waves questions
Penerbit Erlangga.
Science text book B for Grade 8
1. What would be the motion of 1 3/4 vibration of a pendulum will be?
Answer: 1-2-3-2-1-2-3-2
2. A spring mass system moves a-b-c-b-a (b being its center point) its motion is?
Answer: 1 Vibration
3. The number of vibrations performed every second is called?
Answer: The Frequency
4. If 240 Vibrations happens in 2 minutes, its period is?
Answer: 1/2 Seconds
5. A period of a swing is 10 seconds. In every minute, the pendulum performs how many swings?
Answer: 6 Swings
6. If in 1/2 seconds a ruler moves in the pattern a-b-c-b-c, the period of the vibration made by the ruler is?
Answer: 1/2 Seconds
7. If the frequency of a vibration is 300Hz, the period is?
Answer:
P: 1/F
P:1/300
8. A pendulum performs swings with a frequency of 25Hz. The number of Vibrations it can make within a minute is?
Answer: 25x60: 1500
9. Planet Mercury revolves the sun with a frequency of 8x10^-6Hz. The period of planet mercury revolving the sun is?
Answer:
P: 1/F
P:1/8x10^-6 Seconds
10. The number of waves performed in every second is called?
Answer: The Frequency
11. If 30,000 waves are performed in 30 seconds then its frequency is?
Answer:
F: n/t
F:30000/30
F: 1000Hz
12.The time it takes for 2.5 vibrations for a wave is 0.5 seconds, the frequency is?
Answer:
0.5 seconds: 2 vibrations
1 second: 4 vibration
13. If a frequency of a wave is 600Hz and the velocity is 300 m/s, the wavelength is?
Answer:
V: Wl x F
Wl: V/F
Wl: 300/600
Wl: 0.5m
14. 2 vibrations of a wave has a wavelength of 4m and the distance from the furthest point to the other furthest point is 6m. Find the amplitude, wavelength, and frequency if the velocity of the wave is 200 m/s.
Answer:
Amplitude: 6/2: 3m
Wavelength: 4/2: 2m
V: Wl x F
200: 2x F
F: 200/2
F: 100Hz
15. If the vibration direction is perpendicular to the direction of the wave propagation, it means the wave is what wave?
Answer: Transverse Wave
16.The velocity of a wave is 300m/s and its frequency is 450Hz. The wavelength is?
Answer:
V: Wl x F
Wl: V/F
Wl: 300/450
Wl: 2/3m
17. Sound propagates in the air with a speed of 400 m/s. If the frequency of the keynote a is 500 Hz, then the wavelength is?
Answer:
V: Wl x F
Wl: V/F
Wl: 400/500
Wl: 0.8m
Sunday, 14 April 2013
Vibration and waves
Question and answer
http://classjump.com/s/sidiq/documents/Worksheet4VibrationWaves.pdf?
With different values
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. A spring-mass system vibrates exactly 9 times per second. Find its period and its
frequency
1A)
Period = T= 1/9 seconds
Frequency = n/t = 9/1 = 9Hz
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2.A pendulum swings with a period of 1 second.
a. What is its frequency?
2aA) 1/T = 1/1 = 1Hz
b. How many times does it pass the lowest point on its path in 2.0 second? in 79.0 seconds?
2bA) 2times, 79times. Since its 1Hz
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3. A spring-mass system completes 30.0 vibrations in 5.0 seconds, with a 2.0 cm amplitude.
a. Find its frequency and its period.
3aA)
Frequency : 6Hz
Period : 1/6 seconds
b. The same mass is pulled 5.0 cm away from the equilibrium position, then released. What
will the period, the frequency, and the amplitude be?
3bA)
Frequency = 6Hz
Amplitude = 5cm
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4. A pendulum completes 40.0 oscillations per minute. Find its frequency, its period, and its
length.
4A)
Frequency = 40/60 = 2/3 Hz
Period = 1/0.6 = 1.667
Length = Unknown
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5. A clown is rocking on a rocking chair in the dark. His glowing red nose moves back and forth
a distance of 5m exactly 30 times a minute, in a simple harmonic motion.
a. What is the amplitude of this motion?
5/2 = 2.5
b. What is the period of this motion?
T= 1/2.5 = 0.4 Seconds
c. What is the frequency of this motion?
30/60s = 1/2 Hz
d. The top of the clown’s hat contains a small light bulb that shines a narrow light beam. The
beam makes a spot on the wall that goes back and forth between two dots placed 10.00 m
apart as the clown rocks. What are the amplitude, period, and frequency of the spot’s
motion?
Amplitude = 10m / 2 = 5m
Period = 0.4 Seconds (same as 5.b)
Frequency = 1/2Hz (same as 5.c)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
6. A turning fork has a frequency of 256 Hz. The wavelength of the sound produced by the
fork is 46 meters. Calculate the velocity of the waves
Velocity λ x F
= 46m x 256 Hz
=11776 m/s
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
7. Green light has a wavelength of 5.4 x 10-7m and travels through the air at speed of 3 x 108 m/s.
Calculate the period and the frequency of this green light waves.
Period = 1/F = 0.556x 1015
Frequency = v/λ = 3/5.4 x 108 / 10-7 = 0.556 x 1015
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
8. Radio waves travel at the speed of light (3.00 x 108 m/s). An amateur radio system can
receive radio signals at frequencies between 12.00 MHz and 1.20 MHz. What is the range of
the wavelengths this system can receive?
F = 12MHz & 1.2MHz
λ1 = 3x108 / 8 = 3/8 x 108 = 0.375 x 108 Metres
λ2 = V/F2 = 3x108 / 1.2 = 2.5 x 108 Metres
V= λ x F
λ = V / F
http://classjump.com/s/sidiq/documents/Worksheet4VibrationWaves.pdf?
With different values
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. A spring-mass system vibrates exactly 9 times per second. Find its period and its
frequency
1A)
Period = T= 1/9 seconds
Frequency = n/t = 9/1 = 9Hz
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2.A pendulum swings with a period of 1 second.
a. What is its frequency?
2aA) 1/T = 1/1 = 1Hz
b. How many times does it pass the lowest point on its path in 2.0 second? in 79.0 seconds?
2bA) 2times, 79times. Since its 1Hz
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3. A spring-mass system completes 30.0 vibrations in 5.0 seconds, with a 2.0 cm amplitude.
a. Find its frequency and its period.
3aA)
Frequency : 6Hz
Period : 1/6 seconds
b. The same mass is pulled 5.0 cm away from the equilibrium position, then released. What
will the period, the frequency, and the amplitude be?
3bA)
Frequency = 6Hz
Amplitude = 5cm
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4. A pendulum completes 40.0 oscillations per minute. Find its frequency, its period, and its
length.
4A)
Frequency = 40/60 = 2/3 Hz
Period = 1/0.6 = 1.667
Length = Unknown
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5. A clown is rocking on a rocking chair in the dark. His glowing red nose moves back and forth
a distance of 5m exactly 30 times a minute, in a simple harmonic motion.
a. What is the amplitude of this motion?
5/2 = 2.5
b. What is the period of this motion?
T= 1/2.5 = 0.4 Seconds
c. What is the frequency of this motion?
30/60s = 1/2 Hz
d. The top of the clown’s hat contains a small light bulb that shines a narrow light beam. The
beam makes a spot on the wall that goes back and forth between two dots placed 10.00 m
apart as the clown rocks. What are the amplitude, period, and frequency of the spot’s
motion?
Amplitude = 10m / 2 = 5m
Period = 0.4 Seconds (same as 5.b)
Frequency = 1/2Hz (same as 5.c)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
6. A turning fork has a frequency of 256 Hz. The wavelength of the sound produced by the
fork is 46 meters. Calculate the velocity of the waves
Velocity λ x F
= 46m x 256 Hz
=11776 m/s
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
7. Green light has a wavelength of 5.4 x 10-7m and travels through the air at speed of 3 x 108 m/s.
Calculate the period and the frequency of this green light waves.
Period = 1/F = 0.556x 1015
Frequency = v/λ = 3/5.4 x 108 / 10-7 = 0.556 x 1015
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
8. Radio waves travel at the speed of light (3.00 x 108 m/s). An amateur radio system can
receive radio signals at frequencies between 12.00 MHz and 1.20 MHz. What is the range of
the wavelengths this system can receive?
F = 12MHz & 1.2MHz
λ1 = 3x108 / 8 = 3/8 x 108 = 0.375 x 108 Metres
λ2 = V/F2 = 3x108 / 1.2 = 2.5 x 108 Metres
V= λ x F
λ = V / F
Sunday, 7 April 2013
Wave v2
Formulas of velocity of wave
v = S/T
Velocity = S( Distance to be covered (m) ) / T(Covering time (Second) )
v = λ/T
Velocity = Wavelength(λ) / Time
v = S/T
Velocity = S( Distance to be covered (m) ) / T(Covering time (Second) )
v = λ/T
Velocity = Wavelength(λ) / Time
Wave
A wave is
a kind of change that moves from one place to another.
· sound
· water waves
· electromagnetic waves
Longitudinal Waves
In
a longitudinal wave the particle displacement is parallel to the direction of
wave propagation. The animation at right shows a one-dimensional longitudinal
plane wave propagating down a tube. The particles do not move down the tube
with the wave; they simply oscillate back and forth about their individual
equilibrium positions. Pick a single particle and watch its motion. The wave is
seen as the motion of the compressed region (ie, it is a pressure wave), which
moves from left to right.
The P waves (Primary waves) in an
earthquake are examples of Longitudinal waves. The P waves travel with the
fastest velocity and are the first to arrive.
Transverse Waves
In a transverse wave the particle
displacement is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. The
animation below shows a one-dimensional transverse plane wave propagating from
left to right. The particles do not move along with the wave; they simply
oscillate up and down about their individual equilibrium positions as the wave
passes by. Pick a single particle and watch its motion.The S
waves (Secondary waves) in an earthquake are examples of
Transverse waves. S waves propagate with a velocity slower than P waves,
arriving several seconds later.
Electromagnetic Waves
Light,
microwaves, x-rays, and TV and radio transmissions are all kinds of electromagnetic
waves. They are all the same kind of wavy disturbance that repeats itself over
a distance called the wavelength.
Frequency, Period and Amplitude
What is frequency, period and amplitude?
Frequency (f)= the amount of vibration an object makes in 1 second
Period (T)= the amount of time needed in 1 full vibration
Amplitude = the distance between the maximum position of the vibration and the stable/balanced position of a vibration.
SI unit for frequency = Hz (Hertz)
SI unit for period = s (seconds)
Frequency = n/t
-----> T= 1/f or f = 1/t
Period = t/n
Questions:
1. What is the frequency of......
a) 1 second -> 54 vibration?
Answer = 54 ÷ 1 = 54 Hz
b) 5 seconds -> 25 vibration?
Answer = 25 ÷ 5 = 5 Hz
2. What is the period of.......
a) 1 vibration -> 12 seconds?
Answer = 12 ÷ 1 = 12 seconds
b) 5 vibration -> 50 seconds?
Answer = 50 ÷ 5 = 10 seconds
Sunday, 10 March 2013
Vibration
What is vibration:
Vibration is a periodic back-and-forth motion of the particles of an elastic body or medium, commonly resulting when almost any physical system is displaced from its equilibrium condition and allowed to respond to the forces that tend to restore equilibrium.
Real Life examples of vibration:
1. Using a guitar as a musical instrument. The string goes back and forth which makes the sound and also the vibration.
2. Listening to a music through a speaker. The speaker makes sound vibration which makes the sound quality better.
Pendulum and spring:
Examples of real life:
Vibration is a periodic back-and-forth motion of the particles of an elastic body or medium, commonly resulting when almost any physical system is displaced from its equilibrium condition and allowed to respond to the forces that tend to restore equilibrium.
Real Life examples of vibration:
1. Using a guitar as a musical instrument. The string goes back and forth which makes the sound and also the vibration.
2. Listening to a music through a speaker. The speaker makes sound vibration which makes the sound quality better.
Pendulum and spring:
Examples of real life:
Sunday, 24 February 2013
Conservation of Energy
Mechanical Energy
In science, mechanical energy is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy. It is the energy associated with the motion and position of an object. The law of conservation of mechanical energy states that in an isolated system that is only subject to conservative forces the mechanical energy is constant.
Types of Mechanical Energy:
Potential and Kinetic energy
Potential Energy
In physics, potential energy is the energy of an object or a system due to the position of the body or the arrangement of the particles of the system. The SI unit for measuring work and energy is the joule (symbol J).
Formula of Potential energy
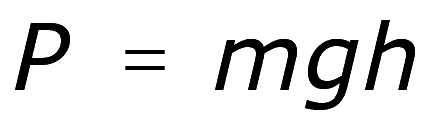
Examples
Case 1: A cat had climbed at the top of the tree. The Tree is 20 meters high and the cat weighs 6kg. How much potential energy does the cat have?
m = 6 kg, h = 20 m, g = 9.8 m/s2(Gravitational Acceleration of the earth)
Step 1: Substitute the values in the below potential energy formula:
Potential Energy: PE = m x g x h
= 6 x 9.8 x 20
Potential Energy: PE = 1176 Joules
Kinetic Energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion. It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity.
Formula of Kinetic energy
Examples
Case 1: Determine the Kinetic energy of a 500kg roller coaster train which moves at a speed of 20 m/s.
M = 500 kg, V = 20 m/s
Step 1: Substitute the values in the below kinectic energy formula:
Kinetic Energy: Ek = ½ mv2
= ½ x 500 x 202
= 0.5 x 500 x 400
Kinetic Energy: Ek = 100000 Joules or 1 x 105 Joules
What is conservation of energy
The law of conservation of energy, first formulated in the nineteenth century, is a law of physics. It states that the total amount of energy in isolated system remains constant over time. The total energy is said to be conserved over time. For an isolated system, this law means that energy can change its location within the system, and that it can change form within the system, for instance chemical energy can become kinetic energy, but that energy can be neither created nor destroyed.
To scientists, conservation of energy is not saving energy. The law of conservation of energy says that energy is neither created nor destroyed. When we use energy, it doesn’t disappear. We change it from one form of energy into another. A car engine burns gasoline, converting the chemical energy in gasoline into mechanical energy. Solar cells change radiant energy into electrical energy. Energy changes form, but the total amount of energy in the universe stays the same. Scientists at the Department of Energy think they have discovered a mysterious new form of energy called "dark energy" that is actually causing the universe to grow!
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)














